What is Molly? Understanding the Popular Party Drug
Molly is a popular name for MDMA, a synthetic drug known for its stimulant and mood-enhancing effects. It is commonly used in parties and music festivals, where it is sought after for creating feelings of euphoria and emotional connection. Many users describe experiences of heightened sensory perception and sociability while under its influence.
Though often perceived as a safer alternative to other drugs, Molly carries significant risks. It can cause serious side effects, including increased heart rate, dehydration, and difficulty regulating body temperature. Understanding the nature and effects of Molly is crucial for anyone considering its use, as well as for those who want to be informed about the substance’s risks.
As discussions surrounding the use of MDMA continue to emerge, it is important to look beyond the allure and explore the realities of Molly. This article will provide insights into its effects, risks, and more, helping readers make informed decisions about this widely-used substance.
Understanding Molly
Molly, a popular recreational drug, has specifics in both its chemical makeup and its history. Knowing these details can help users and their families understand its effects and risks.
Chemical Composition
Molly is another name for MDMA, scientifically known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine. This compound is a synthetic substance that combines stimulant and hallucinogenic effects. It primarily affects the brain by increasing the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
- Serotonin: Enhances mood and emotion.
- Dopamine: Increases feelings of pleasure.
- Norepinephrine: Raises heart rate and blood pressure.
Users may experience heightened senses and feelings of emotional connection. However, these effects come at a cost, as they can lead to anxiety, dehydration, and dangerous spikes in body temperature.
Historical Context
MDMA was first synthesized in 1912 by Anton Köllisch, a German chemist. Initially, it was researched for potential medical uses, such as controlling bleeding during surgery.
In the late 1970s, MDMA gained popularity as a recreational drug. It became known for its role in party scenes and music festivals. Today, it’s often found in tablets or capsules branded as “Molly” or “Ecstasy.” These names can create confusion, as the purity and strength of these substances can vary significantly.
The changing perspectives on its use and risks continue to shape the conversation around Molly. Understanding its history helps clarify why it attracts both users and researchers today.
Effects and Risks
Molly, a popular form of MDMA, can lead to various physiological and psychological effects. While some users seek its euphoric sensations, it is essential to understand the potential health risks associated with its use.
Physiological Effects
Molly affects the body by increasing heart rate and blood pressure. Users often experience heightened energy and improved sensory perception.
Some common physiological effects include:
- Increased heart rate: This can range from mild to severe, putting stress on the cardiovascular system.
- Elevated body temperature: Known as hyperthermia, this can also lead to dehydration.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some users experience gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Muscle tension: Many report clenching their jaws or tightness in muscles.
When combined with other substances, the risks can increase significantly, making it critical for users to be aware of these effects.
Psychological Effects
Molly has notable psychological impacts, which can vary from person to person. Many users report feelings of euphoria, increased empathy, and a sense of connection with others.
Key psychological effects include:
- Mood elevation: Users often experience intense happiness, which can lead to risky behaviors.
- Altered perception: This can include changes in sensory experiences, such as enhanced colors and sounds.
- Anxiety and paranoia: After the effects wear off, some users may experience negative feelings, leading to mood swings.
- Memory issues: Some studies suggest MDMA can impair memory or cognitive functions over time.
Awareness of these psychological effects is crucial for anyone considering its use.
Potential Risks
The risks associated with Molly are significant and should not be overlooked. Many of these can have lasting effects on health.
Notable risks include:
- Addiction: Repeated use can lead to dependence.
- Long-term cognitive impairment: Studies have linked MDMA to memory and learning issues.
- Hyperthermia: Elevated body temperature can be life-threatening when not managed.
- Interaction with other drugs: Mixing Molly with alcohol or certain prescriptions can increase health risks.
Understanding these potential risks is vital for anyone contemplating using Molly and highlights the importance of making informed choices.
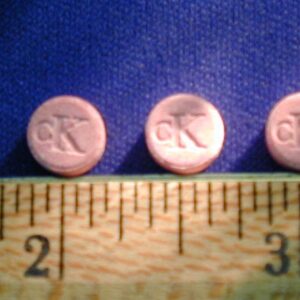
What Does Molly Look Like?
Molly, also known as MDMA, comes in many forms. Sometimes, it looks like a white or brown powder, while other times it can be found as crystals. People might also see it sold as colorful pills or tablets, often stamped with logos or designs. These designs can make it look harmless, but it is still a dangerous drug. Because Molly is made illegally, it’s hard to know what’s really in it. This makes it even riskier to use. Additionally, the varied forms that it comes in can make it hard to identify. Here are some examples of the different pill forms that Molly (MDMA) can come in:

Photos from the official DEA website.
Usage and Prevalence
Molly, a popular name for MDMA, has become common in social settings, especially among young adults. Understanding who uses it and the trends in its use provides insight into its impact on society.
Demographics of Use
Molly is mostly popular among young adults aged 18 to 25. This age group often attends parties, music festivals, and nightclubs where the drug is frequently used.
Research shows that about 3.5% of high school seniors reported using MDMA in the past year. Usage is more prevalent in urban areas, where nightlife is vibrant.
Gender also plays a role; studies indicate that men are slightly more likely to use Molly compared to women.
Patterns and Trends
Recent years have seen a rise in the popularity of Molly. Many users report taking it at music festivals and raves, enhancing their social experiences.
The purity and form of Molly can vary greatly. It often comes in capsules, tablets, or powder, making it easy for users to consume.
Growing concerns about harmful effects lead some states to educate the public on risks. There is evidence that as awareness increases, some users are starting to seek safer alternatives.
While the overall perception of Molly changes, it remains a significant issue in discussions about drug use and public health.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Molly, a popular recreational drug, raises important legal and ethical questions. Understanding these aspects helps users and society navigate the complex landscape surrounding its use.
Legal Status
Molly, scientifically known as MDMA, is classified as a Schedule I drug in the United States. This designation means it has a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use. Possession, distribution, or manufacturing of MDMA is illegal and can result in significant penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
Some states have pursued legislation to allow MDMA for therapeutic use in controlled settings. These proposals highlight growing recognition of potential therapeutic benefits, especially for conditions like PTSD. However, the legal framework remains strict, and any changes to its status will continue to face considerable scrutiny.
Ethical Implications
The ethical considerations surrounding Molly’s use are multifaceted. One major concern is the potential for harm, both to users and society. Users often risk their health by consuming unregulated substances that may contain harmful additives.
Moreover, there are ethical questions about access to information regarding harm reduction. Providing education and resources promotes safer use practices. Advocates argue that informed users can make better choices, reducing negative outcomes.
Lastly, there is an ongoing debate about the responsibility of drug manufacturers and distributors. Ensuring the safety and efficacy of drugs is crucial in preventing addiction and health crises within communities. The balance between personal freedom and public health remains a significant ethical challenge.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common questions about MDMA, covering its effects, mental health implications, potential for addiction, legal status, interactions with other substances, and emergency procedures related to its use.
What are the effects of using MDMA?
MDMA typically produces feelings of euphoria, increased energy, and enhanced sensory perception. Users may feel more emotionally open and connected to others. Physical effects can include raised heart rate, increased body temperature, and jaw clenching.
How does the use of MDMA influence mental health?
MDMA can lead to both short-term and long-term mental health effects. While some users report positive feelings and enhanced mood during use, it may also cause anxiety, depression, or confusion afterward. Repeated use can affect mood and emotional regulation over time.
Can MDMA be considered addictive, and what are the risks of addiction?
MDMA is not classified as a physically addictive substance, but it can lead to psychological dependence. Users may develop cravings and feel compelled to use it more often. Risks include potential withdrawal symptoms and negative impacts on mental health with prolonged use.
What is the legal status of MDMA in different countries?
In many countries, including the United States, MDMA is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance. This means it is illegal to manufacture, distribute, or possess it. Legal status varies internationally, with some nations allowing research or medicinal use.
How does MDMA interact with other substances or medications?
MDMA can have dangerous interactions with other drugs, including alcohol and certain medications. Mixing MDMA with substances like antidepressants or stimulants increases the risk of serious side effects, including serotonin syndrome, which can be life-threatening.
What should someone do in the case of an MDMA-related emergency?
If someone is experiencing a medical emergency due to MDMA use, it is crucial to seek immediate help. This may include calling emergency services or taking the individual to a hospital. Staying calm and providing as much information as possible to medical personnel is essential.